Today I'd be happy to provide a explanation of Fuel cell vehicles.
A fuel cell vehicle (FCV) is a type of electric vehicle that uses a fuel cell stack to generate electricity to power an electric motor. This stack consists of multiple cells that contain an anode, cathode, and electrolyte membrane. Hydrogen gas is supplied to the anode, while oxygen is supplied to the cathode. The hydrogen molecules are split into protons and electrons, which pass through the electrolyte membrane. The electrons flow through an external circuit to generate electricity, while the protons combine with the oxygen and electrons to form water, which is emitted as the only byproduct.
Fuel cell vehicles offer several advantages over conventional gasoline or diesel vehicles. They produce zero harmful emissions, as the only byproduct is water, which is environmentally friendly. They are also highly efficient, with a fuel economy comparable to that of conventional vehicles, and they can be refueled in a matter of minutes, similar to gasoline vehicles. Additionally, they offer quiet and smooth operation, as they do not have a combustion engine.
However, there are some challenges to widespread adoption of fuel cell vehicles. One of the main challenges is the lack of hydrogen refueling infrastructure, which can limit their availability in certain regions. Additionally, they require costly components, including the fuel cell stack and hydrogen storage tanks. These costs can make fuel cell vehicles more expensive than conventional vehicles, although there are efforts to reduce the costs through advancements in technology and production processes.
Despite these challenges, there is growing interest in fuel cell vehicles as a sustainable transportation option, particularly in areas with high air pollution levels and a strong renewable energy infrastructure. Major automakers such as Toyota, Hyundai, and Honda have already introduced fuel cell vehicles to the market, and more are expected to follow in the coming years. How it Work
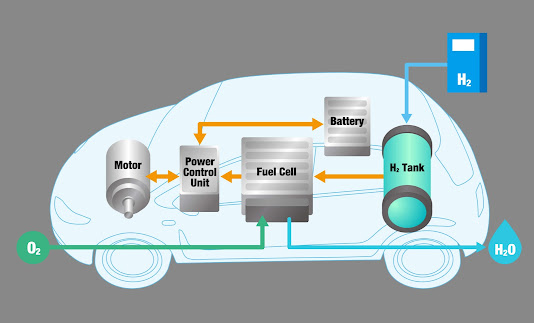
A fuel cell vehicle (FCV) works by using a fuel cell stack to convert hydrogen and oxygen into electrical energy, which is used to power an electric motor. Here's a more detailed explanation of how it works:
Fuel: Hydrogen gas is stored in a high-pressure tank in the vehicle.
Oxygen: Air is drawn into the vehicle through a grille at the front, and the oxygen in the air is used in the fuel cell stack.
Fuel Cell Stack: The fuel cell stack is made up of multiple cells, each containing an anode, cathode, and electrolyte membrane. Hydrogen gas is supplied to the anode, while oxygen is supplied to the cathode. The hydrogen molecules are split into protons and electrons, which pass through the electrolyte membrane. The electrons flow through an external circuit to generate electricity, while the protons combine with the oxygen and electrons to form water, which is emitted as the only byproduct.
Electric Motor: The electricity generated by the fuel cell stack is used to power an electric motor that drives the wheels of the vehicle.
Power Control Unit: The power control unit manages the flow of electricity between the fuel cell stack and the electric motor, and also controls the charging of the battery used for auxiliary power.
Battery: A small battery is used to provide auxiliary power for the vehicle, such as for powering the lights and other electrical systems.
Regenerative Braking: When the driver applies the brakes, the electric motor switches to a generator mode, capturing the kinetic energy of the vehicle and converting it into electricity, which is stored in the small auxiliary battery.
Overall, a fuel cell vehicle offers several advantages over conventional gasoline or diesel vehicles, including zero harmful emissions, high efficiency, and quiet and smooth operation. However, challenges such as the lack of hydrogen refueling infrastructure and high costs of components currently limit the widespread adoption of fuel cell vehicles.
It has any future is real life?
Yes, fuel cell vehicles (FCVs) do have a future in real life, as they offer several advantages over conventional gasoline or diesel vehicles, including zero harmful emissions, high efficiency, and quiet and smooth operation.
Many automakers are investing in fuel cell technology and have introduced fuel cell vehicles to the market, including Toyota, Honda, Hyundai, and Mercedes-Benz. Additionally, governments around the world are promoting the use of fuel cell vehicles as part of their efforts to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and improve air quality.
There are also ongoing efforts to address the challenges facing the widespread adoption of fuel cell vehicles, such as the lack of hydrogen refueling infrastructure and the high cost of fuel cell components. Advances in technology and production processes are helping to reduce the cost of fuel cell components, while initiatives are underway to expand hydrogen refueling infrastructure in certain regions.
Overall, while fuel cell vehicles currently make up a small portion of the global vehicle market, there is growing interest in them as a sustainable transportation option, particularly in areas with high air pollution levels and a strong renewable energy infrastructure. As technology continues to improve and infrastructure expands, it is likely that we will see an increase in the adoption of fuel cell vehicles in the coming years.
Thanks For Read out article ..Follow us on social media 1)Facebook Page







Leave a Comment